Menu
- Spring Graduation Ceremonies 2025
- SRC Online Elections 2025
- Application & Registration Information
- Academic Calendar 2025
- Fees Booklet
- Academic Calendar 2026
- Study Opportunities
- ENVISION2030 Institutional Awards
- Career Leaflets
- Handbooks
- Court Order – Forums Threat
- ENVISION2030
- Why Choose DUT
- “Missing Middle” application form
- NSFAS New Students
- NSFAS
- Autumn Graduation Ceremonies 2025
- Honorary Doctorates
- DUTLink Newsletter
- Lecture Timetable
- Association of Commonwealth Universities
DUTLINK
Our Facebook Page
| Home | Indumiso Heatpump Project | Steve Biko Power Factor Corrections | Alpine Residence Hot Water | Student Solar Charging Stations | LED Lighting Initiative |
Hot Water and HVAC Interventions
Geysers consume the most electricity on the DUT campuses, second to air conditioning systems, so turning them off is effective when trying to control the peak demand and prevent load shedding. Load shedding is what happens whenever there Is an unplanned shortfall in the country’s electricity supply.
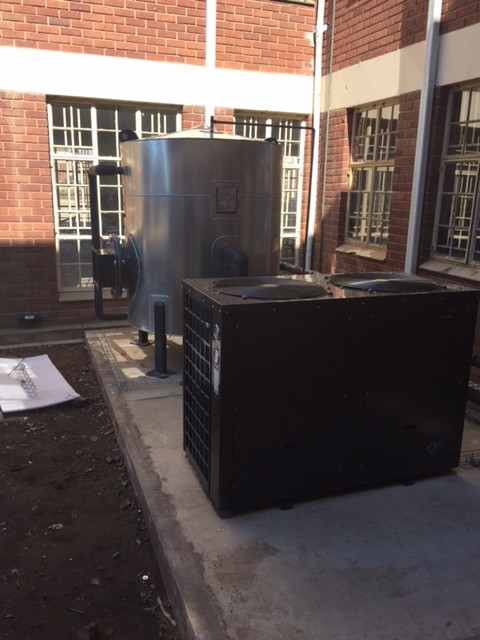
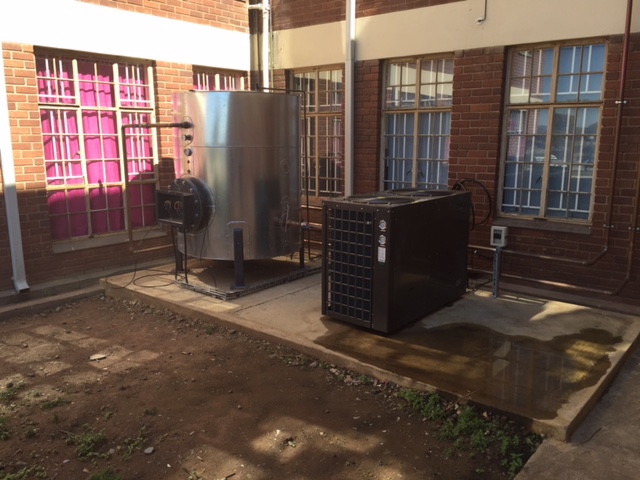
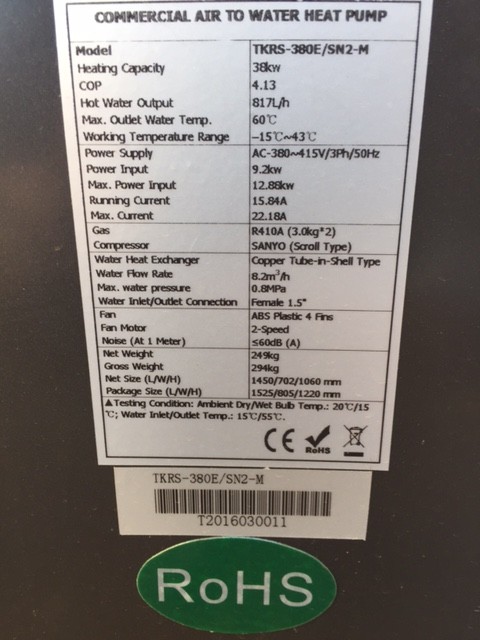
A Heat Pump offers you a way to use electricity to heat water efficiently. Where a geyser uses three units of electrical energy to produce three units of heat energy, a Heat Pump converts just one unit of electrical energy into three units of heat energy. A Heat Pump uses a small amount of energy to move heat from one medium to another, using mechanical work to move heat from a low temperature source to a high temperature sink. There are two types of Heat Pump systems namely the integrated type and the split type. In the first case the entire system is contained in one unit and consists of a storage tank and a Heat Pump.
In the second configuration the tank is separated from the Heat Pump. Heat Pumps use the reverse cycle of a refrigeration plant to heat water. In effect, it transfers heat from a source such as air or water to the water which is to be heated. As in other refrigeration equipment, the Heat Pump system employs an evaporator, a compressor, a condenser, refrigerant gas, and an expansion valve within a closed circuit. Latent heat is given off when the refrigerant gas is liquefied through the condenser and transferred to the surrounding water together with further “sensible” heat loss, effectively raising the temperature of water to a higher temperature.
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
